Dec 18, 2025
Dilemma of Aspirants preparing for Government school Teacher recruitment Exams
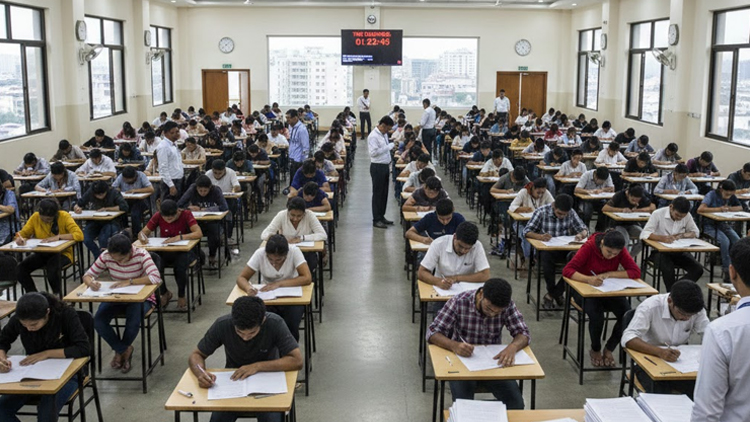
Aspirants preparing for government school teacher recruitment exams (like TET/CTET, state TETs, KVS/NVS, DSSSB, etc.) commonly struggle in a few recurring areas. Understanding these early helps candidates plan better. Here are the main weaknesses and concern areas, grouped clearly:
- Pedagogy & Child Development (CDP): Most underestimated section Common issues:
- Rote learning of theories without understanding application
- Confusion between psychologists (Piaget vs Vygotsky vs Kohlberg)
- Difficulty in scenario-based questions
- Poor grasp of inclusive education, special needs, and learning disabilities
Why it matters: This section often carries high weightage Questions are conceptual, not factual
- Subject Content Gaps: Especially in upper primary & secondary levels Typical problems:
- Weak conceptual clarity in core topics (Maths, Science, Social Science, Languages)
- Over-reliance on guidebooks instead of NCERT
- Inability to solve application-based or higher-order questions
Example: Maths aspirants struggling with basic algebra/number sense Science aspirants mixing concepts in physics/biology Language aspirants lacking grammar fundamentals
- Language Proficiency: Frequently ignored but scoring Issues include:
- Weak grammar and vocabulary
- Poor comprehension skills
- Difficulty in pedagogy of language (how children learn languages)
- Confusion between first language vs second language teaching methods
- Lack of Exam-Oriented Practice: Knowledge without performance Common mistakes:
- Not practicing enough MCQs Avoiding previous years’ papers
- Poor time management during the exam Inability to eliminate wrong options
- Teaching Aptitude & Classroom Application: Main problem is that they face difficulty in applying concepts to classroom situations. They have weak understanding of:
- Classroom management
- Assessment methods (formative vs summative)
- Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE)
- Misunderstanding the role of a facilitator vs instructor
- Inadequate Understanding of Educational Policies and Static GK trap: Aspirants often:
- Memorize facts without context
- Are unaware of recent reforms (NEP 2020, RTE Act provisions)
- Confuse policies, years, and objectives
- Psychological & Strategic Issues: Silent but critical weaknesses which includes: Exam anxiety Lack of consistency
- Poor revision strategy
- Following too many sources
- Unrealistic expectations or burnout
- Digital & Modern Teaching Skills: Many aspirants:
- Are uncomfortable with ICT in education
- Lack awareness of online/blended learning tools
- Are unfamiliar with assessment via digital platforms
How Successful Aspirants Overcome These Weaknesses: Successful aspirants overcome the common weaknesses in government teacher recruitment exams by adopting focused, exam-oriented strategies that target each area of difficulty. Here’s how they address the key challenges:
- Pedagogy & Child Development (CDP)
Top performers actively engage with real-life classroom scenarios and avoid rote learning by:
- Preparing concise notes and revising them regularly to reinforce understanding.
- Practicing previous years’ papers and mock tests to become familiar with conceptual and scenario-based questions.
- Seeking guidance from experienced teachers to clarify complex theories and their practical applications.
- Using real-life examples to connect theory with classroom situations, making learning more meaningful.
- Subject Content Gaps
Successful candidates ensure conceptual clarity by:
- Studying NCERT textbooks as the primary resource and supplementing with guidebooks for advanced practice.
- Identifying and addressing their specific content gaps through targeted revision and practice.
- Solving application-based and higher-order questions to build confidence in problem-solving.
- Language Proficiency
High scorers strengthen language skills by:
- Practicing exam-specific strategies such as time management, skimming, and scanning for reading comprehension.
- Engaging in authentic practice with past papers, sample questions, and online resources.
- Building vocabulary and grammar through consistent reading, conversation practice, and use of language learning apps.
- Exam-Oriented Practice
Winners emphasize regular practice and strategic revision:
- Solving a large number of MCQs and previous years’ papers to improve speed and accuracy.
- Mimicking exam conditions during practice sessions to build stamina and time management skills.
- Reviewing mistakes and focusing on weak areas for improvement.
- Teaching Aptitude & Classroom Application
Aspirants who succeed:
- Apply pedagogical concepts to classroom scenarios through case studies and practical examples.
- Understand assessment methods and classroom management by observing or shadowing experienced
- Focus on continuous and comprehensive evaluation (CCE) and facilitator roles, rather than rote instruction.
- Educational Policies
Top candidates:
- Study recent reforms (like NEP 2020 and RTE Act) in context, not just as isolated facts.
- Use infographics and summaries to memorize and differentiate between various policies and their objectives.
- Psychological & Strategic Issues
Successful aspirants manage stress and maintain consistency by:
- Developing a structured revision schedule and avoiding burnout.
- Using self-evaluation and feedback to track progress and adjust strategies.
- Limiting sources and focusing on quality over quantity in their preparation.
- Digital & Modern Teaching Skills
They stay updated by:
- Familiarizing themselves with ICT tools and digital assessment platforms through online courses and tutorials.
- Practicing with digital mock tests and exploring blended learning resources.
By addressing each of these areas systematically, aspirants not only overcome their weaknesses but also build a strong foundation for long-term teaching success.